Electrolyte-supported cells
by KERAFOL®
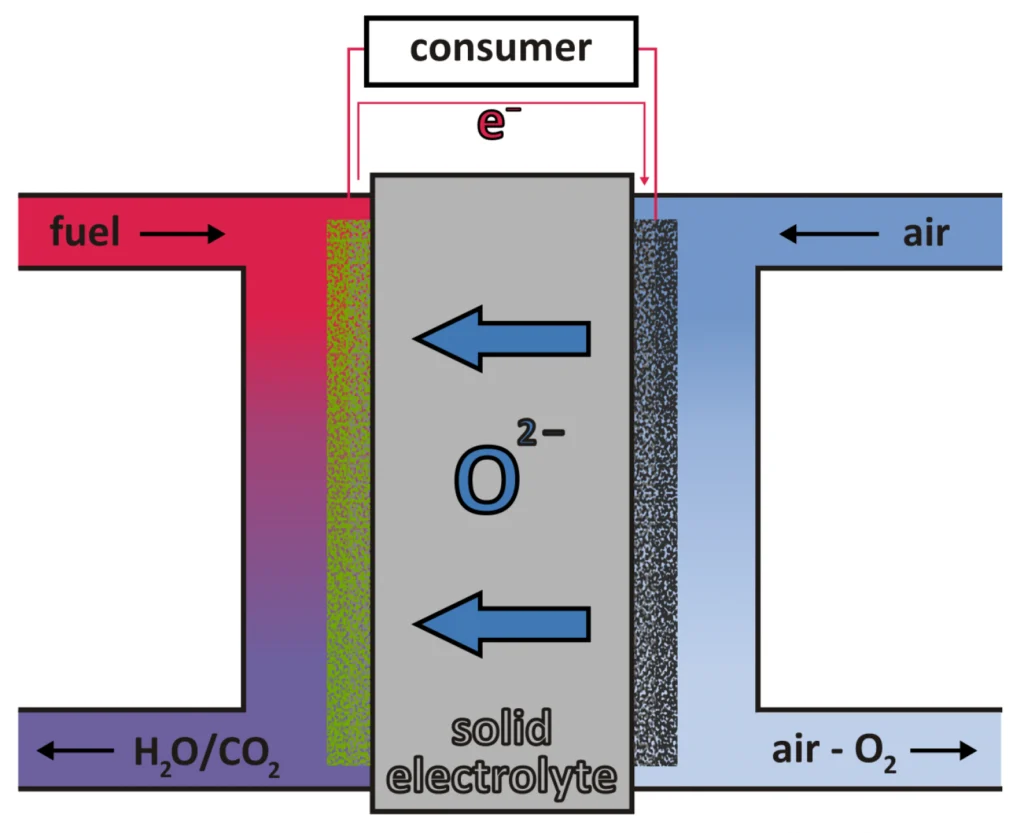
The ESC consists of an electrolyte that spatially separates the anode and cathode and conducts oxygen ions at high operating temperatures of 750 – 950°C. On the cathode side, oxygen molecules are absorbed from the gas phase in an electrochemical reaction and oxygen ions are formed with electrons from the cathode. The oxygen ions move through the electrolyte to the anode side where they react with hydrogen, releasing electrons to the anode to form water. The two reactions create a positive excess charge at the cathode and a negative excess charge at the anode, which can be drawn in form of an electric current. In order to achieve higher electrical voltages, several cells are connected in series to form a so-called stack, which is the current-supplying unit.
Variants
Electrolyte-supported substrates
Our electrolyte-supported cells have high planarity and are optimized for use in SOC stacks. Efficient electrodes with low polarization resistances were developed for this purpose. The robustness of the cells has been proven in several long-term tests as well as with thermal cycles and in reduction/oxidation cycle tests.
The R&D department is constantly optimizing the power density of the cells and their robustness. In addition, the KeraCell III cell type with an LSCF oxygen electrode was developed, which provides a high power density as a fuel and electrolysis cell.
- Oxygen electrode: LSM or LSCF
- Hydrogen electrode: NiO/YSZ or NiO/GDC
- Electrolyte substrates: 3YSZ, 8YSZ, 6ScSZ, 10Sc1CeSZ, YScSZ
Dimensions
according to customer requirements
We offer electrolyte-supported cells in the standard formats 50 x 50 mm² and 100 x 100 mm². On customer request, a variety of round and rectangular geometries can be realized as well as the production of symmetrical cells and half cells depending on the geometry.

Zellen


